Published On: 20 June 2025
Category: Clinical Trial I Infectious Disease I
Gut and Gastrointestinal Infections
Written By: Pharmacally Medical News Desk
.
Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is among the most challenging hospital-acquired infections globally. C.Difficile, known for its high recurrence rates and significant impact on the gut microbiome. To date, vancomycin has long been a standard treatment; however, it lacks selectivity and often disrupts beneficial gut bacteria, which contributes to relapses.
Ibezapolstat, a first-in-class antibiotic being developed by AcurX Pharmaceuticals, aims to decipher these issues. Unlike traditional broad-spectrum agents, Ibezapolstat specifically targets DNA polymerase IIIC, an enzyme essential for the replication of Gram-positive bacteria like C. difficile, which is absent in beneficial anaerobic flora.
The recently published Phase 2b clinical trial results in The Lancet Microbe mark a crucial step forward in this drug’s journey, offering new hope in reducing recurrence and treating serious hospital-acquired infections like Clostridioides difficile.
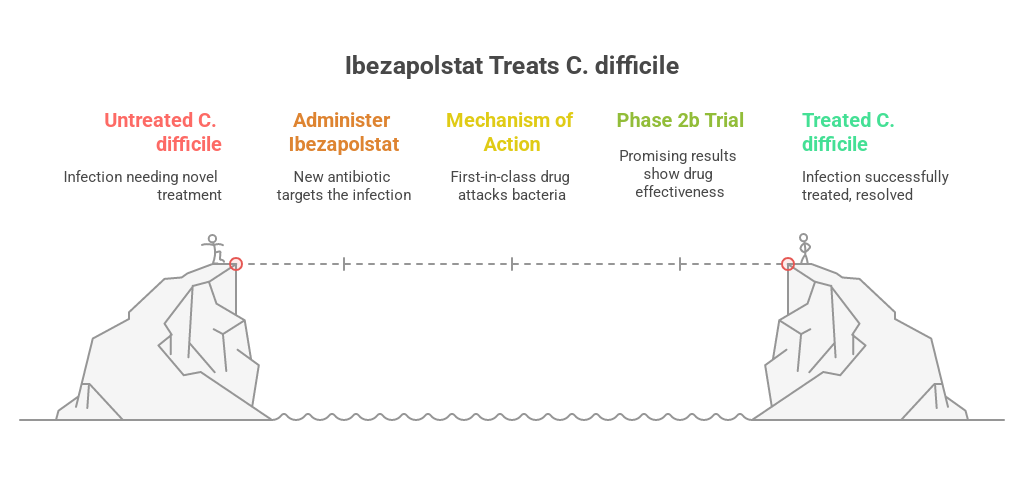
The Phase 2b Trial: Design & Goals
AcurX Pharmaceutical recently concluded its phase 2b trial, and the results are published in Lancet Microbes. The trial was conducted across 15 U.S. centers between March 2021 and October 2023. The randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial enrolled adults aged 18 to 90 with confirmed C. difficile infection. Patients were randomly assigned to receive
- Ibezapolstat 450 mg orally every 12 hours (n = 18 total; 16 included in the efficacy analysis)
- Vancomycin 125 mg orally every 6 hours (n = 14)
The primary objective was clinical cure at the end of treatment (EOT), defined as the resolution of diarrhea and no need for further CDI therapy 48 hours post-treatment.
Efficacy: A Match for Vancomycin
In the Phase 2b clinical trial, ibezapolstat demonstrated clinical efficacy that was analogous to vancomycin, which is the current standard of care for Clostridioides difficile infection. Among the patients evaluated in the trial, 94% of patients treated with ibezapolstat achieved complete clinical cure at the end of treatment, while 100% of patients receiving vancomycin met the same endpoint. This slight numerical difference was not statistically significant and met the criteria for non-inferiority, establishing Ibezapolstat as an equally effective treatment option. More compelling, however, were the findings from a pooled analysis of data from both the Phase 2a and 2b trials. In pooled analysis, done from the combined dataset of Phases 2a and 2b, ibezapolstat achieved a clinical cure rate of 96%. Surprisingly, ibezapolstat sustained a cure rate of 100%, meaning no recurrences were observed one month after treatment. This is in contrast to historical data for vancomycin, where recurrence rates range from 26% to as high as 58%. These results position ibezapolstat not only as an equally effective treatment as vancomycin for acute CDI but also as a promising candidate for reducing the risk of relapse, a critical issue in current CDI management.
Microbiome and Bile Acid Profiles
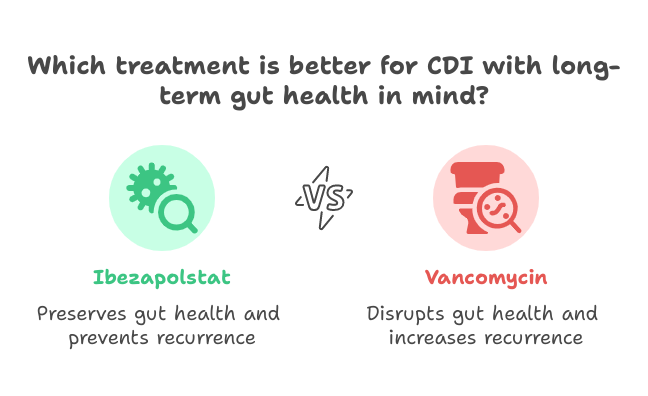
Even if ibezapolstat showed comparable clinical efficacy to vancomycin, ibezapolstat shows significant advantages over vancomycin in terms of protecting gut health, which is an essential factor in preventing recurrent infections. One of the prominent findings from the study was the rapid microbiological clearance of C. difficile, with 94% of patients treated with ibezapolstat showing eradication of the organism by Day 3, compared to 71% in the vancomycin group. But the main differentiation lies in ibezapolstat’s ability to save the beneficial gut microbiota. Unlike vancomycin, which broadly disrupts the intestinal flora, ibezapolstat preserved vital bacterial groups such as the Firmicutes and Actinobacteria phyla known for supporting immune function and maintaining colonization resistance. This preservation of the microbiome might play a role behind why Ibezapolstat showed zero recurrence rates.
Additionally, stool analysis revealed that ibezapolstat favorably altered bile acid profiles, reducing primary bile acids (which promote C. difficile germination) and increasing secondary bile acids (which inhibit it). This bile acid shift further enhances the gut’s natural defense against reinfection.
These microbiome and metabolomic findings highlight ibezapolstat’s potential not just to treat CDI effectively, but to do so in a way that supports long-term gut health and prevents recurrence, something current therapies generally fail to achieve.
Safety & Pharmacokinetics
Ibezapolstat demonstrated a favorable safety profile in the Phase 2b trial. No drug-related serious adverse events, treatment discontinuations, or deaths were reported in either the ibezapolstat or vancomycin treatment groups.
Pharmacokinetic analysis further supported its targeted mechanism of action, with ibezapolstat achieving high concentrations in stool exceeding 1,000 μg/g by days 8 to 10 while showing minimal systemic absorption. This gut-localized exposure is particularly advantageous in treating C. difficile infections, as it maximizes local antimicrobial activity while minimizing the risk of systemic side effects or toxicity.
The Unique Mechanism of Action
Unlike vancomycin, which largely disrupts bacterial cell wall synthesis and also affects a wide range of gut bacteria due to its common mechanism pathway through inhibiting cell wall synthesis, ibezapolstat offers a more targeted line of attack. It selectively inhibits DNA polymerase IIIC (PolC), an enzyme essential for the replication of Gram-positive pathogens like C. difficile but absent in human cells and many beneficial gut bacteria. This precision targeting enables ibezapolstat to kill C. difficile effectively while showing mercy on much of the gut’s healthy microbiota. As a result, it minimizes disruption to colonization resistance, the gut’s natural defense against reinfection. This selective mechanism is increasingly being recognized as the gold standard in modern antimicrobial development, aligning efficacy with microbiome preservation.
The Road to Approval
Ibezapolstat has already received the U.S. FDA Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) and Fast Track designations, accelerating its development and review timeline. At the same time, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recognized AcurX Pharmaceuticals with Small and Medium-sized Enterprise (SME) status, offering additional guidance and regulatory incentives. A global Phase 3 trial is currently in development and is expected to enroll over 600 patients. This pivotal study will compare ibezapolstat directly with vancomycin in a larger and more diverse population to confirm its efficacy and safety on a broader scale. A crucial regulatory meeting with the FDA is scheduled for mid-2025 to finalize the Phase 3 development plan and determine the path toward potential market approval.
Conclusion & Pharmacally Take
Current treatments for CDI have improved outcomes, but eradicating C. Difficile, preventing recurrence, and protecting other gut microbiomes continue to be major hurdles, “but ibezapolstat offers a new hope in this direction. With its narrow-spectrum precision, gut microbiome-sparing effects, and potential to prevent relapse, it addresses the shortcomings of traditional CDI therapies like vancomycin.
If Phase 3 results confirm these findings, ibezapolstat could emerge not just as an alternative but as a preferred first-line therapy for initial and recurrent CDI.
At Pharmacally, we’re closely watching ibezapolstat’s development as a milestone in microbiome-conscious antibiotic therapy. Its success could pave the way for a new era of targeted antimicrobials that treat without extra damage.
References
Taryn A Eubank, Jinhee Jo, M Jahangir Alam, et al, Efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics, and associated microbiome changes of Ibezapolstat compared with vancomycin in adults with Clostridioides difficile infection: a phase 2b, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, multicentre study, Lancet Microbe 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.lanmic.2025.101126
Acurx Announces Publication in Lancet Microbe of Phase 2b Clinical Trial Data for Ibezapolstat in CDI, AcurX pharmaceuticals, 17 June 2025, https://www.acurxpharma.com/news-media/press-releases/detail/111/acurx-announces-publication-in-lancet-microbe-of-phase-2b
Acurx Announces Publication in Lancet Microbe of Phase 2b Clinical Trial Data for Ibezapolstat in CDI, PRNewswire, 17 June 2025, https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/acurx-announces-publication-in-lancet-microbe-of-phase-2b-clinical-trial-data-for-ibezapolstat-in-cdi-302483504.html