24 June 2025
Category: Clinical Trial I Obesity & Metabolic Disorders I
Diabetes and Weight loss
Medically Written and Reviewed By:
Vikas Londhe MPharm

The race to develop new treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes is getting more and more competitive. To this race, the results of the REDEFINE 2 trial (NCT05394519), published recently in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). The study highlights the powerful potential of a novel combination therapy, CagriSema. This once-weekly subcutaneous treatment, combining cagrilintide (an amylin analogue) and semaglutide (a GLP‑1 receptor agonist), has shown impressive results for weight loss and glycemic control, especially in individuals with both obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Study at a Glance
The REDEFINE 2 trial (Trial No. NCT05394519) is a Phase 3a, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study sponsored by Novo Nordisk, conducted across 12 countries in Europe, North America, and Asia. The study was designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of CagriSema. CagriSema was administered once weekly in dose dose-escalated manner starting from a 0.25 mg dose and increasing stepwise till it reached 2.4 mg for each drug in 16 weeks. The trial enrolled non-insulin-dependent participants aged 18 years or older with a body mass index of 27 kg/m² or more, HbA1c between 7% and 10%, and at least one self-reported unsuccessful dietary effort to lose weight. The lifestyle modifications were also suggested to study participants. Participants were randomly assigned to receive CagriSema (cagrilintide 2.4 mg + semaglutide 2.4 mg) or placebo over a 68-week treatment period, followed by a 7-week follow-up. The primary endpoint was percentage change in body weight and percentage of patients achieving ≥5% weight loss from baseline to week 68; however, additional secondary endpoints included changes in waist circumference, glycated hemoglobin level, systolic blood pressure, and other physical function measures from baseline to 68 weeks. Results from this trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, have shown the potential of CagriSema to offer a new standard of care in obesity and diabetes management.
Key Findings
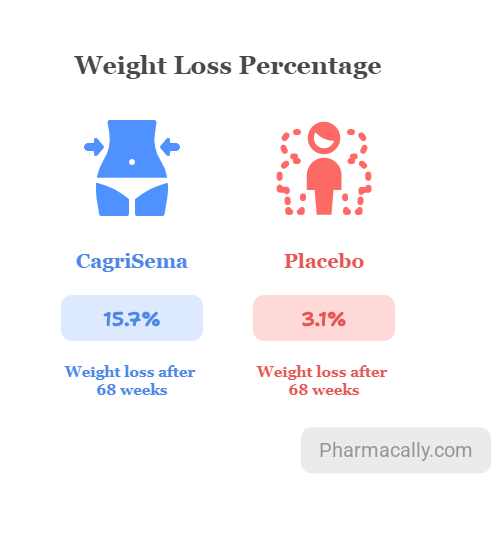
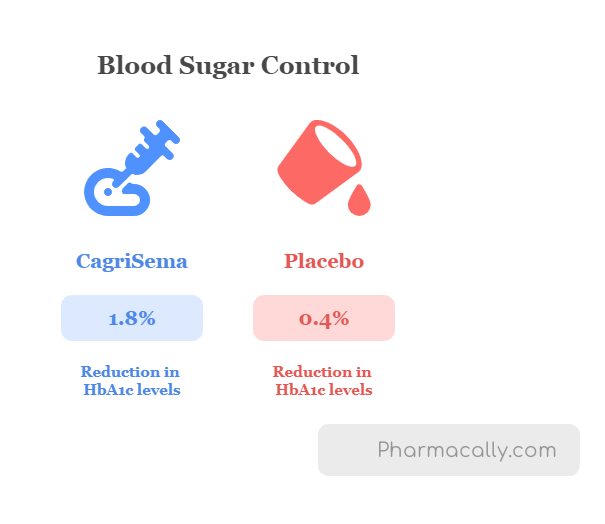
The REDEFINE 2 trial showed that CagriSema led to significantly greater weight loss and better blood sugar control compared to placebo in people with obesity and Type 2 diabetes. After 68 weeks of treatment, patients receiving CagriSema lost an average of 15.7% of their body weight, which was much higher than the placebo group’s 3.1%. In addition, almost 83.6% of patients in the CagriSema group achieved at least 5% weight loss, a clinically significant benchmark, compared to 30.8% in the placebo group. Additionally, a weight reduction of 10% or more occurred in 65.6% of the patients in the cagrilintide–semaglutide group and in 10.3% of in the placebo group; a weight reduction of 15% or more occurred in 43.8% and 2.4%, respectively, and a weight reduction of 20% or more occurred in 22.9% and 0.5%, respectively. CagriSema also showed greater improvement in blood sugar control, reducing average HbA1c levels by 1.8 percentage points, while the placebo reduced them by only 0.4 percentage only.
On average, systolic pressure went down by 4.1 mm Hg more than the placebo group, a statistically significant difference. Additionally, the combination treatment also showed improvements in diastolic blood pressure, C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation), and cholesterol levels compared to placebo. On average, waist size reduced by 8.3 cm more than the placebo group.
These results confirmed that the combination therapy offers stronger benefits for both weight and glucose management, especially in patients with diabetes.
Mechanism of Action
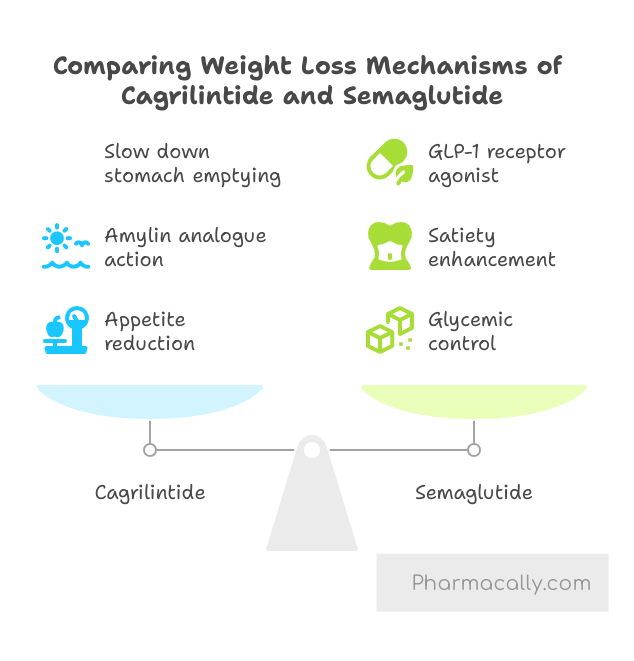
Cagrilintide is an amylin analogue, which mimics the action of the natural hormone amylin. It helps to reduce appetite, increase feelings of fullness, and slow down the emptying of the stomach, which leads to reduced food intake and promotes weight loss. It binds to amylin receptors in the brain, specifically in the hypothalamus and other brain regions, to promote feelings of fullness and reduce food intake. On the other hand, semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, a class of drugs that stimulates insulin release in response to high blood sugar levels, suppresses glucagon (a hormone that raises blood sugar), and also delays gastric emptying. It plays a dual role in improving glycemic control and enhancing satiety, contributing further to weight reduction. Together, cagrilintide and semaglutide produce synergistic effects.
Safety Profile
CagriSema was generally well tolerated, with a safety profile consistent with what is typically seen with GLP‑1 receptor agonists like semaglutide. The most common side effects reported were gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These side effects were mostly mild to moderate in severity. A slightly higher number of participants in the CagriSema group discontinued treatment due to side effects compared to the semaglutide and placebo groups. Importantly, no new safety concerns emerged during the trial.
Future Plan
Following the strong results from REDEFINE 2, Novo Nordisk is expected to seek regulatory approval for CagriSema in 2026, supported by earlier data from the REDEFINE 1 trial, which showed an even greater weight loss of 22.7% in people without diabetes. The company is also developing a pre-filled pen for convenient once-weekly dosing, aiming to simplify treatment and enhance patient adherence.
Conclusion and Pharmacally’s Take
CagriSema may emerge as a landmark treatment after approval for diabetes management and obesity care. It combines the benefits of two powerful drugs from their class, offering patients a more effective and synergistic approach to weight and glucose control. This trial proves that individuals with type 2 diabetes, who typically lose less weight than those without, can achieve meaningful and substantial weight loss.
With semaglutide already a blockbuster and tirzepatide on the rise, CagriSema could be the next market capturer in metabolic health and weight loss, especially for patients with complex comorbidities.
References
Davies MJ, Bajaj HS, Broholm C, et al, Cagrilintide–Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes, The New England Journal of Medicine, Published June 22, 2025, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2502082
A Research Study to See How Well CagriSema Helps People with Type 2 Diabetes and Excess Body Weight Lose Weight (REDEFINE 2), ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05394519, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05394519
Garvey WT, Blüher M, Contreras CKO, et al, Coadministered Cagrilintide and Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity, The New England Journal of Medicine, Published June 22, 2025, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2502081

