Written By: Pharmacally Medical News Desk
Johnson & Johnson MedTech has received FDA approval for an expanded indication of its TRUFILL n‑BCA Liquid Embolic System for embolization of the middle meningeal artery (MMA) as an adjunct to surgery in patients with symptomatic subacute and chronic subdural hematoma (cSDH). This approval represents an important regulatory milestone, supporting the emerging role of MMA embolization in cSDH management, particularly among older adults where the condition is increasingly common.
Christian Cuzick, President, Worldwide Neurovascular, Johnson & Johnson MedTech, stated that the approval underscores the long-standing clinical value of TRUFILL n‑BCA and reflects the company’s commitment to advancing neurovascular technologies for complex conditions like cSDH.
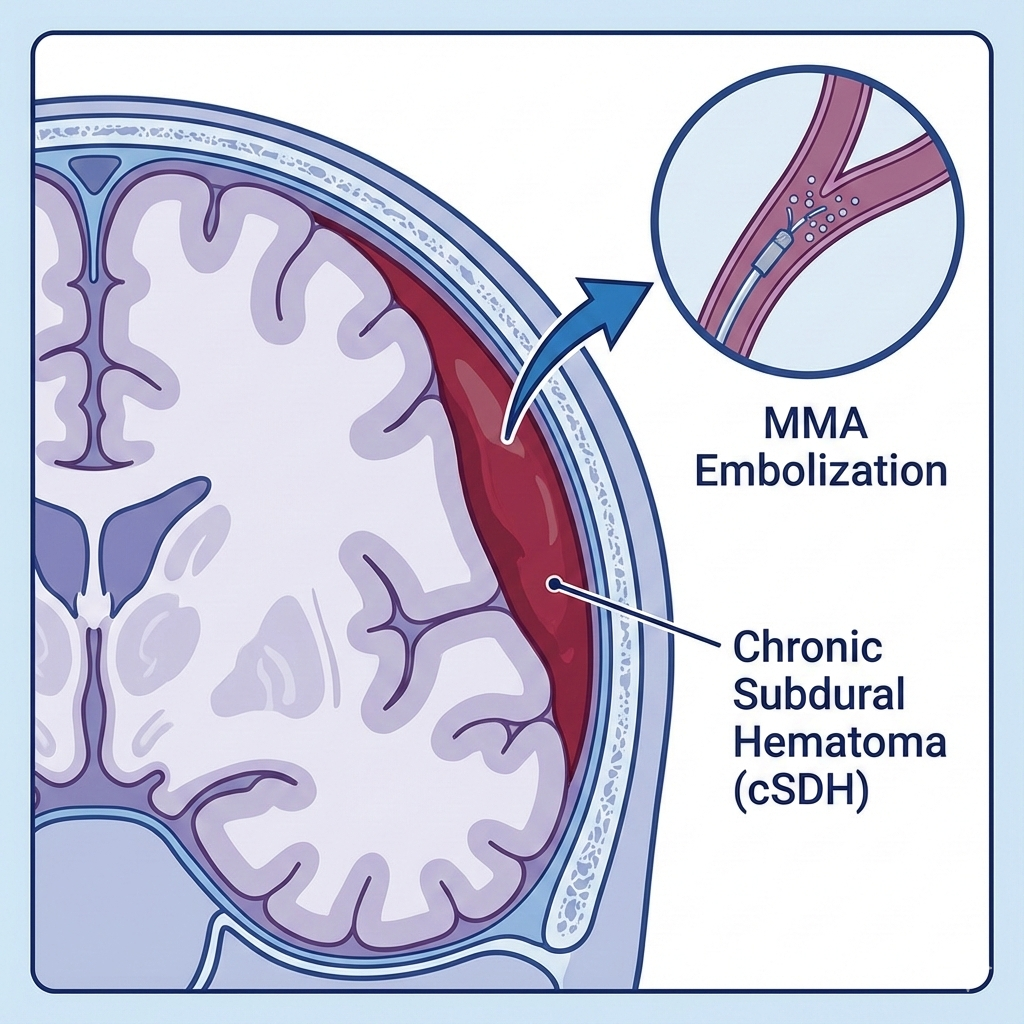
Understanding Chronic Subdural Hematoma
Chronic subdural hematoma arises from slow venous bleeding between the brain and its outer covering, often after minor head trauma, and commonly presents with headaches, cognitive changes, gait disturbance, or focal neurological deficits. Burr-hole drainage remains the traditional standard treatment but carries recurrence rates of 10–30%, especially in elderly patients or those on anticoagulants.
TRUFILL n‑BCA Liquid Embolic System Overview
The TRUFILL n‑BCA (n-butyl cyanoacrylate) Liquid Embolic System is a fast-acting agent that polymerizes on contact with blood, enabling durable vessel occlusion; it has been used for years in neurovascular and peripheral embolization procedures. In cSDH, it targets the MMA to reduce blood flow to fragile neovasculature in hematoma membranes, promoting resolution and lowering recurrence risk.
Clinical Evidence from the MEMBRANE Trial
The approval draws on the MEMBRANE randomized controlled trial (NCT04816591), which evaluated TRUFILL n‑BCA-based MMA embolization versus standard of care. The trial’s primary effectiveness endpoint was a composite of residual or re-accumulation of cSDH >10 mm at 6 months or need for re-operation within 6 months; TRUFILL n‑BCA demonstrated superior effectiveness with an odds ratio of 0.475 in the surgical cohort.
In RCTs and large observational MMA embolization series using n‑BCA, high technical success rates exceed 95%, with recurrence in single-digit to low-teen percentages lower than historical surgical benchmarks and reduced need for repeat interventions
Clinical Outcomes and Safety Profile
Patients often show improvement or stabilization in neurological symptoms like headache and gait issues, alongside favorable functional outcomes on modified Rankin Scale scores. In published n‑BCA MMAE series, complication rates are low (around 2–3%), with adverse events consistent with known embolization risks; serious issues like non-target embolization remain uncommon.
The FDA stresses proper patient selection, operator expertise, and adherence to instructions for use.
Dr. Christopher P. Kellner, Director of Cerebrovascular & Intracerebral Hemorrhage Programs at Mount Sinai and MEMBRANE investigator, noted that the trial addressed an unmet need in high-risk cSDH patients and demonstrated a favorable treatment effect for TRUFILL-based MMA embolization over standard care.
References
Johnson & Johnson Receives FDA Approval for TRUFILL n‑BCA Liquid Embolic System for the Treatment of Symptomatic Chronic Subdural Hematoma, 18 December 2025, https://www.jnj.com/media-center/press-releases/johnson-johnson-receives-fda-approval-for-trufill-n-bca-liquid-embolic-system-for-the-treatment-of-symptomatic-chronic-subdural-hematoma
Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Subdural Hematomas With TRUFILL® n-BCA (MEMBRANE), ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT04816591, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04816591
Christopher P. Kellner et al, Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization with n‐Butyl Cyanoacrylate for the Treatment of Subdural Hematomas: The MEMBRANE Study Design, Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology, Volume 5, Number 6, https://doi.org/10.1161/SVIN.125.001828
Abdelsalam A, et al, Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization for Chronic Subdural Hematoma Using N-Butyl Cyanoacrylate with a D5W Push Technique: A Multicentric North American Study of 269 Patients. Oper Neurosurg. 2025 Jun 1;28(6):817-823. doi: 10.1227/ons 0000000000001369. Epub 2024 Sep 23. PMID: 39311581; PMCID: PMC12273647.
Abdelsalam A, Sanikommu S, Ramsay I, et al LB-013 Middle meningeal artery embolization for chronic subdural hematoma using n-BUTYL cyanoacrylate with D5W push technique: a multicentric North American study of 269 patients. Journal of NeuroInterventional Surgery 2024;16:A275-A277.