01 July 2025
Category: Surgical Technology I Robotic Surgery I
Robotic Knee Surgery
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Dinesh Patil (MBBS, D-Ortho)
Knee and Hip Arthroplasty specialist surgeon
Assisted By: Dewanshee Ingale
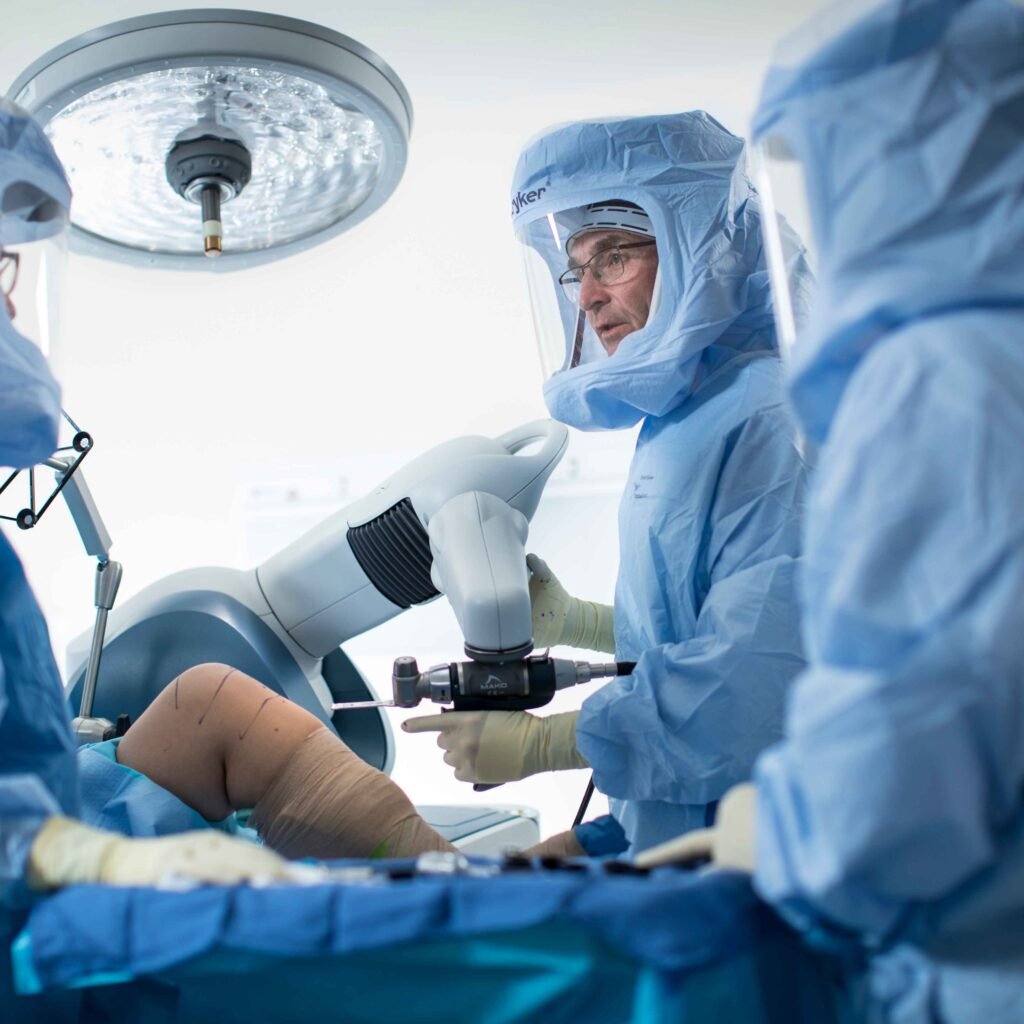
Knee replacement surgery has made significant progress in the past few years, offering relief and flexibility to the majority of people who suffer from serious joint pain and arthritis. The integration of robotic technology has made advancements in joint replacement, especially knee surgery, to new heights of precision and efficacy. Robotic-assisted knee replacement surgery has transformed the way orthopaedic surgeries are performed, providing numerous benefits to patients and orthopaedic surgeons.
What is Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement Surgery
Robot-assisted knee replacement surgery is a new method that uses the most advanced robotic technology and the expertise of an experienced orthopedic surgeon. The robots used in this procedure are either fully automated or semi-automated. It is an extremely refined device that helps the surgeon. The use of robotic technology offers immediate feedback, enhanced visualization, and precise control, which permits the surgeon to position and align the knee implant more precisely than with conventional methodologies.
Surgeons either use a CT scan-driven 3D model of the patient’s knee joint or use an X-ray and their own experience to mark anatomical landmarks. By using either plan, the orthopedic surgeon creates an individualized surgical plan to adapt to the unique anatomy of each patient. The robotic arm simply directs the surgeon’s movements, making sure the bone cuts and implant positioning are implemented with submillimeter accuracy. The systems also allow for enabling adjustments as needed and real-time feedback for optimal results.
With the use of the integration of robotic technology with the experience of excellent orthopedic surgeons, the margin of error, trauma associated with the adjacent tissues are minimized, and it is easy to create a personalized approach for each patient. Resulting in safer, more convenient, and more reliable knee replacement with the ability to recover fast and serve for long-term benefits.
CT Scan-Guided vs Non-CT Scan-Guided Knee Replacement
As advancements in knee replacement surgical techniques evolve, a key distinction has emerged in how these surgeries are planned and executed, like CT scan-guided versus non-CT scan-guided approaches. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice generally depends on the patient’s condition, the surgeon’s expertise, and available resources.
CT scan-guided or image-based knee replacement involves preoperative 3D imaging, usually using a computed tomography (CT) scan. This scan helps generate a patient-specific surgical plan, customized to the individual’s bone anatomy and alignment. In CT scan-guided knee replacement, a detailed scan of the knee is used to create a 3D model of the patient’s knee anatomy. This model helps the surgeon to plan the surgery with high precision by selecting the optimal implant size, position, and alignment. In many cases, custom surgical tools or cutting guides are also 3D-printed based on this data to ensure a perfect fit.
Non-CT scan-guided knee replacement surgery relies on standard X-rays, manual instruments, and the surgeon’s understanding of anatomical landmarks, without the use of preoperative 3D imaging. This traditional approach has been widely used for decades and continues to deliver excellent clinical outcomes in a broad range of patients. It is cost-effective, readily available in most hospitals, and does not expose patients to additional radiation. While it may involve more intraoperative judgment and variability in implant positioning, experienced surgeons can achieve highly successful and durable results using this method.
Fully Automated vs Semi-Automated Knee Replacement Procedures
Depending on the level of technological integration, these procedures can be categorized into fully automated and semi-automated systems, each with its degree of precision, control, and surgeon involvement.
Fully automated systems refer to highly advanced robotic platforms capable of executing surgical tasks with minimal manual intervention. These systems use preoperative imaging (such as CT or MRI scans) to generate a precise 3D model of the patient’s knee, and then autonomously guide or perform steps like bone cutting and implant positioning based on the surgical plan.
Semi-automated procedures are the current standard in robotic-assisted knee replacements. In these surgeries, the robot acts as a guide or assistant, helping the surgeon perform tasks more accurately rather than executing them independently. Semi-automated knee replacement combines real-time navigation with robotic guidance to enhance surgical precision. The surgeon remains in full control, using robotic assistance based on preoperative or intraoperative imaging (CT or imageless systems).
How Does Robotic-Assisted Knee Surgery Work
Preoperative Planning
The process of the knee replacement starts with complete imaging, which involves conducting CT scans or X-rays, which helps the robotic technology to create a detailed and personalized 3D model of the patient’s knee. The obtained 3D model is beneficial for the surgeon to plan a systematic plan for mapping out the precise bone-cutting procedure and implant positioning and its size according to the patient’s distinctive anatomy.
Surgical Guidance
During the surgery, the patient is anesthetized, and to access the knee joint, a small incision is made. The robotic system is then established and synced with the preoperative 3D model. As the surgeon proceeds with the surgery, the robotic arm offers real-time feedback and suggestions to make sure every minute action aligns with the developed surgical plan. The system observes and maintains a proper alignment according to the plan, aids in making accurate bone cuts, and evaluates the soft tissue balance during the procedure.
Enhanced Accuracy
The data-driven approach of the robotic system allows for highly precise placement of the knee implant, enhancing the fitting and the function of the prosthetic joint. The level of precision minimizes the risk of complications, including implant misalignment or asymmetric wear, and results in the easy, quick, and smooth recovery of the patients.
Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Knee Surgery

Proven Precision and Customisation
The robotic-assisted knee replacement uses high-tech imaging and computerized systems to create a 3D image of the knee. And thus patients can plan and implement performing the surgery with submillimeter precision, adapting the position of the implant to the patient’s distinctive anatomy. The research has developed a robotic technology to enhance the correctness of implant orientation, which enhances the long-term results and aids in longer implant life and faster recovery of the patients, and leads to increased patient acceptability.
Reduced Recovery Time
The robotic-assisted knee replacement surgery usually needs minor incisions and leads to reduced trauma to the adjacent tissues. The robotic technology provides a correctness that offers improved soft tissue management. This characteristic of the system helps in better patient tolerability due to the decreased postsurgical ache and discomfort, decreases the blood loss, and also reduces the hospital stay. Hence, it offers patients the chance to start recovery and return to the daily routine a lot faster than a patient who was conventionally operated on.
Increased Patient Satisfaction
Multiple surveys and patient studies were conducted with those undergoing the robotic-assisted knee replacement, which reported increased satisfaction rates. This technology supports improved joint function, reduced aches, and a faster and very easy recovery.
Enhanced Safety and Reduced Complications
The robotic-assisted technology offers up-to-date data and assistance in surgery. Reducing the complications associated with the surgery, such as wrong implant placement or unnecessary bone degradation. The integrated robotic technology lowers the risk of complications and problems associated with surgeries like infection, blood loss, and the need for revision surgery. Consequently, this technology offers overall safety of patient.
Clinical Applications and Case Studies
Malla Reddy Narayana Hospital saw 4-5 successful robotic knee replacement surgeries within weeks of implementing the technology, resulting in less soft tissue damage and early mobilization. On a larger scale, Narayana Health City performed 300 robotic knee replacements over six months, treating patients across 31 Indian districts and 10 other countries.
Challenges and Considerations
Robotic systems are known to show improved results, for which there must be exclusive training in surgeries and maintaining procedural proficiency. Malla Reddy Narayana Hospital has counteracted this via several simulated surgeries and compliance with the international safety protocol. Cost remains a challenge, but institutions are continually making efforts to enhance it through scalable infrastructure.
The Patient Experience

Robotic-assisted knee operation redefines the patient’s journey, allowing smoother and easier recovery comparable to the conventional procedure, hence aiding patients in readily accepting surgery. The surgery is usually done under the effect of anesthesia, which may be general or local, making sure that the patients don’t suffer from pain and feel relaxed throughout the operation.
Hospital stay is the most important factor that makes a patient rethink undergoing surgery, and hence, patients prefer robotic-assisted knee replacement. The most remarkable advantage of this advanced technique is the decreased hospital stay. The majority of people return home in a single day or two post-surgery because of the minor cuts performed during the operation. Same-day discharge is also possible in cases with less complexity and healthy individuals, hence permitting patients to begin recovering at their own homes.
The notable characteristic of robot-assisted surgeries is that patients experience minimal pain and fear because of the minor incisions and correct technique used, which remarkably improves recovery. This methodology supports quick mobilization, with many patients who are able to stand and start walking with support within hours after the surgery.
The patient is started on physiotherapy after the surgery, mostly on the same day or the next morning. Immediate recovery is very important for the restoration of joint movement, fostering strength, and helping with a rapid shift to daily routine. The mixture of reduced postsurgical pain, faster movement, and quick physiotherapy offers a high level of patient satisfaction.
In general, the patient experience is characterized by less pain associated with the joint, fear, and shorter hospital stays, which makes robotic-assisted technology knee replacement a preferred choice in orthopedic patients.
Future Directions
The primary focus of the robotic-assisted knee replacement is fostering customized, efficient, and easily accessible care. One of the significant advancements is the development of custom implant libraries, permitting the surgeons to choose implants as per the unique anatomy of the patient’s knee. Hence, it leads to improved fit and function. The most important development is the combination of predictive analytics with the use of data and artificial intelligence; surgeons are able to predict results and hence personalize recovery plans, leading to faster and more effective recovery. Finally, the ongoing cost reduction measures focus on making the robotic-assisted operations affordable. With the advancing technology and increasing applications, these efforts will continue to make robotic surgery open to a larger number of patients and healthcare organizations. Altogether, these trends are coming together to create a future in which the robotic knee replacement is safer, more accurate, and available to all.
References
Advances in Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement Surgery https://www.narayanahealth.org/blog/robotic-orthopaedic-surgery
Saber AY, Marappa-Ganeshan R, Mabrouk A. Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564396/
Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery: Types, Procedure, Technology, Benefits, and Risks https://poonahospital.org/blog/robotic-knee-replacement-surgery/
Mobility Matters: Narayan Health City Performs 300 Robotic Knee Replacements in Six Months https://www.healthcareexecutive.in/blog/mobility-matters
Fu X, She Y, Jin G, Liu C, Liu Z, Li W, Jin R. Comparison of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Robot Surg. 2024 Jul 25;18(1):292. Doi: 10.1007/s11701-024-02045-y. PMID: 39052153; PMCID: PMC11272701.
Aneja K, Rudraraju RT, Shyam A. Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: Innovations, Precision, and the Future of Joint Reconstruction. Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2024 December;14(12): 04-07.
Advances in Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement Surgery https://www.narayanahealth.org/blog/advances-in-robotic-assisted-knee-replacement-surgery
Mancino F, Fontalis A, Kayani B, Magan A, Plastow R, Haddad FS. The current role of CT in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2024 Sep 1;106-B(9):892-897. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.106B9.BJJ-2023-1303.R1. PMID: 39216858.
Robotic Knee Replacement: Advantages and Disadvantages, Care CHL Hospital, https://www.carehospitals.com/indore/blog-detail/general/robotic-knee-replacement